How to Migrate from Odoo 18 to Odoo 19: Step-by-Step Guide
Odoo
5 MIN READ
October 8, 2025
![]()

Migrating to a new version of Odoo can be a game-changer for your business, unlocking enhanced features, improved performance, and better security. Odoo 19 introduces several structural and functional updates that streamline operations, but it also requires careful handling of code and database changes to avoid disruptions. In this blog, we’ll walk you through the key steps for a smooth upgrade from Odoo 18 to 19, incorporating essential technical adjustments shared by our tech team. Whether you’re a developer, IT admin, or business owner, this guide will help you navigate the Odoo migration process efficiently.
We’ll cover major areas like model changes, field renamings, deprecated features, and specific module updates. By following these Odoo upgrade best practices, you can minimize downtime and ensure compatibility.
Let’s dive in!
Why Upgrade to Odoo 19?
Before jumping into the technical details, it’s worth noting the benefits of migrating to Odoo 19. This version offers advanced AI integrations, refined user interfaces, and optimized workflows for modules like Sales, Accounting, and Inventory. Key improvements include faster report generation, enhanced mobile responsiveness, and better data integrity. However, the upgrade involves breaking changes that could impact custom modules, so thorough testing in a staging environment is crucial. Always back up your database and code before starting the Odoo version migration.
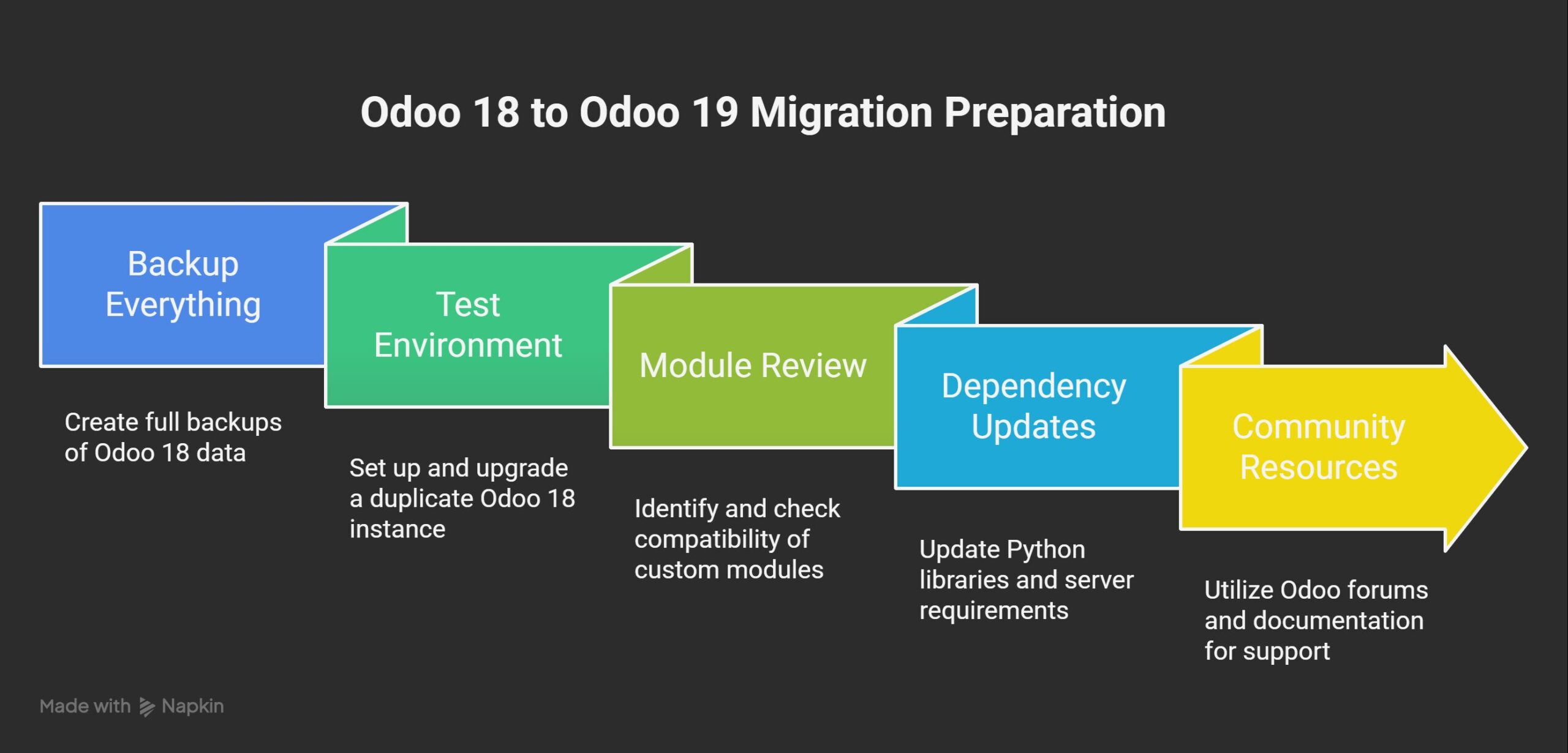
Preparing for the Migration
To ensure a seamless transition:
- Backup Everything: Create full backups of your Odoo 18 database, files, and custom code.
- Test Environment: Set up a duplicate Odoo 18 instance and upgrade it first.
- Module Review: Identify custom modules and check for compatibility with Odoo 19 APIs.
- Dependency Updates: Update Python libraries and ensure your server meets Odoo 19 requirements (e.g., Python 3.10+).
- Community Resources: Leverage Odoo forums, documentation, and migration scripts for additional support.
Now, let’s address the specific technical changes.
General Technical Changes in Odoo 19
Odoo 19 refines several core elements for better modularity and performance. Here are the key updates:
- Category from res.groups: Categories in res.groups have been restructured for clearer privilege management.
- Group_ids changed field in ir.ui.menu: The group_ids field in ir.ui.menu has been updated to reflect new access control mechanisms.
- Group id changes in res users: Group IDs in res.users now align with the new privilege system.
- The type=’json’ in http route is changed to type=’jsonrpc’: HTTP routes using type=’json’ must be updated to type=’jsonrpc’ for compatibility.
- _name = ‘res.partner.title’ model removed: The res.partner.title model has been deprecated and removed; migrate any related data to alternative structures.
- from odoo import registry changed to from odoo.modules.registry import Registry: Import statements for registry access have been modularized.
- from odoo.tools.misc import xlsxwriter changed to import xlsxwriter: Simplified import for XLSX handling.
- Module group categories: res.groups are now res.groups.privilege: Group categories are now handled via res.groups.privilege for enhanced granularity.
- Ir.actions.server cannot not use sudo and group_ids at the same time: Avoid combining sudo with group_ids in server actions to prevent conflicts.
- <kanban-box> to <card></card></kanban-box>: Kanban views now use <card> instead of <kanban-box> for modern UI consistency.
- tax_id to tax_ids: Single tax fields have been pluralized to support multiple taxes.
- product_uom to product_uom_id: UoM fields now reference IDs directly for better relational integrity.
- registry updated with Registry: from odoo import registry: from odoo.modules.registry import Registry: Consistent registry imports across the system.
- factor field to relative_factor: Renamed for clarity in unit conversions.
- category_id to relative_uom_id: Direct linking replaces category-based UoM associations.
- expand=”0″ string=”Group By” removed: Simplified group tags in search views.
- json to jsonrpc: Aligns with the HTTP route change for JSON handling.
- mobile field removed from res.partner: The mobile field in res.partner is no longer available; use phone or custom fields.
- self._context to self.env.context: Environment context access standardized.
- groups_id changed to group_ids: Pluralized for consistency.
- query = self._where_calc(domain) self._apply_ir_rules(query) changed to query = self._search(domain, bypass_access=True): Simplified query building with access bypass.
- Users changed to user_ids: Relational fields updated for multi-user support.
- self._where_calc(domain) changed to self._search(domain, bypass_access=True): Streamlined domain searching.
- from odoo.tools.misc import xlsxwriter changed to import xlsxwriter: Repeated for emphasis on import changes.
- _apply_ir_rules is removed from v19: Rules application integrated into search methods.
- FormView controller requires the’mode’ prop in debug mode: Explicit mode specification in debug for FormViews.
- from odoo.modules.module import get_module_resource(18) -> from odoo.modules import get_resource_from_path(19): Resource path handling updated.
- Deprecated odoo.osv.Expressions -> odoo.fields.Domain: Use odoo.fields.Domain for expressions.
- Changed _web_client_readonly(self) -> _web_client_readonly(self, rule, arg): Additional parameters for readonly checks.
- Deprecated self._uid -> self.env.uid: Environment-based UID access.
- Updated ir.ui.menu where the fields are now updated based on action_id,action_model parameters instead of just action: More precise menu configurations.
- Changed authenticate(request.session.db, creds) -> authenticate(request.env, creds): Environment-driven authentication.
Additionally:
- res.users: Groups now have been removed from res. users model file and is made into a separate new Model.
- res.groups:
- Removed in 19:
- Class Group Impelled
- Changed in 19:
- Class Groups:
- category_id -> privilege_id.category_id
- users -> user_ids
- Class Groups:
- Introduced in 19:
- Privileges
- Removed in 19:
- Removed _sql_constraints
- Deprecated odoo.osv.Expressions -> odoo.fields.Domain
- Changed _web_client_readonly(self) -> _web_client_readonly(self, rule, arg)
- Deprecated self._uid -> self.env.uid
- Updated ir.ui.menu where the fields are now updated based on action_id,action_model parameters instead of just action.
- Changed authenticate(request.session.db, creds) -> authenticate(request.env, creds)
These changes promote cleaner code and reduce deprecated warnings during your Odoo 18 to 19 migration.
UoM Changes
Unit of Measure (UoM) handling has been overhauled in Odoo 19 for direct relationships and simplicity.
Highlights
- uom.category table removed.
- uom_type field removed from uom.uom.
- factor_inv field renamed to relative_factor.
- Use relative_uom_id to link units directly.
Example Migration
Odoo 18
xml
<record id="product_uom_cubic_cm" model="uom.uom">
<field name="name">cm³</field>
<field name="category_id" ref="uom.product_uom_categ_vol"/>
<field name="factor_inv">28.3168</field>
<field name="uom_type">bigger</field>
</record>
Odoo 19
xml
<record id="product_uom_cubic_cm" model="uom.uom">
<field name="name">cm³</field>
<field name="relative_factor">28.3168</field>
<field name="relative_uom_id" ref="uom.product_uom_litre"/>
</record>
This shift eliminates redundant categories, making UoM configurations more intuitive during your Odoo upgrade.
Res Groups Changes
Group management is now more privileged-focused, enhancing security and organization.
Highlights
- Field Renamed: category_id → privilege_id
- Model Change: ir.module.category now connects through res.groups.privilege
- In res.groups, you cannot use ir.module.category directly. It is now referenced via res.groups.privilege.
Example Migration
Odoo 18
xml
<record id="base.module_category_sales_sales" model="ir.module.category">
<field name="description">Helps you handle your quotations, sale orders and invoicing.</field>
<field name="sequence">1</field>
</record>
<record id="group_sale_salesman" model="res.groups">
<field name="name">User: Own Documents Only</field>
<field name="category_id" ref="base.module_category_sales_sales"/>
<field name="implied_ids" eval="[(4, ref('base.group_user'))]"/>
<field name="comment">the user will have access to his own data in the sales application.</field>
</record>
Odoo 19
xml
<record model="ir.module.category" id="module_category_sales">
<field name="name">Sales</field>
<field name="sequence">5</field>
</record>
<record model="res.groups.privilege" id="res_groups_privilege_sales">
<field name="name">Sales</field>
<field name="sequence">1</field>
<field name="category_id" ref="base.module_category_sales"/>
</record>
<record id="group_sale_salesman" model="res.groups">
<field name="name">User: Own Documents Only</field>
<field name="sequence">10</field>
<field name="privilege_id" ref="res_groups_privilege_sales"/>
<field name="implied_ids" eval="[(4, ref('base.group_user'))]"/>
<field name="comment">the user will have access to his own data in the sales application.</field>
</record>
These updates improve role-based access control (RBAC) in Odoo 19.
Sale Order Line Changes
Sales modules see refinements for better tax and UoM handling.
Highlights
- Field Renamed
- product_uom -> product_uom_id
- tax_id -> tax_ids
Apply these to your sale.order.line models to avoid errors.
Account Changes
Accounting features have been streamlined.
Highlights
- Field Removed
- deprecated
Search View Highlights
- No Extra parameter in group tag
- <group expand=”0″ string=”Group By”> (v18)</group>
- <group> (v19)</group>
These simplify views and remove obsolete fields.
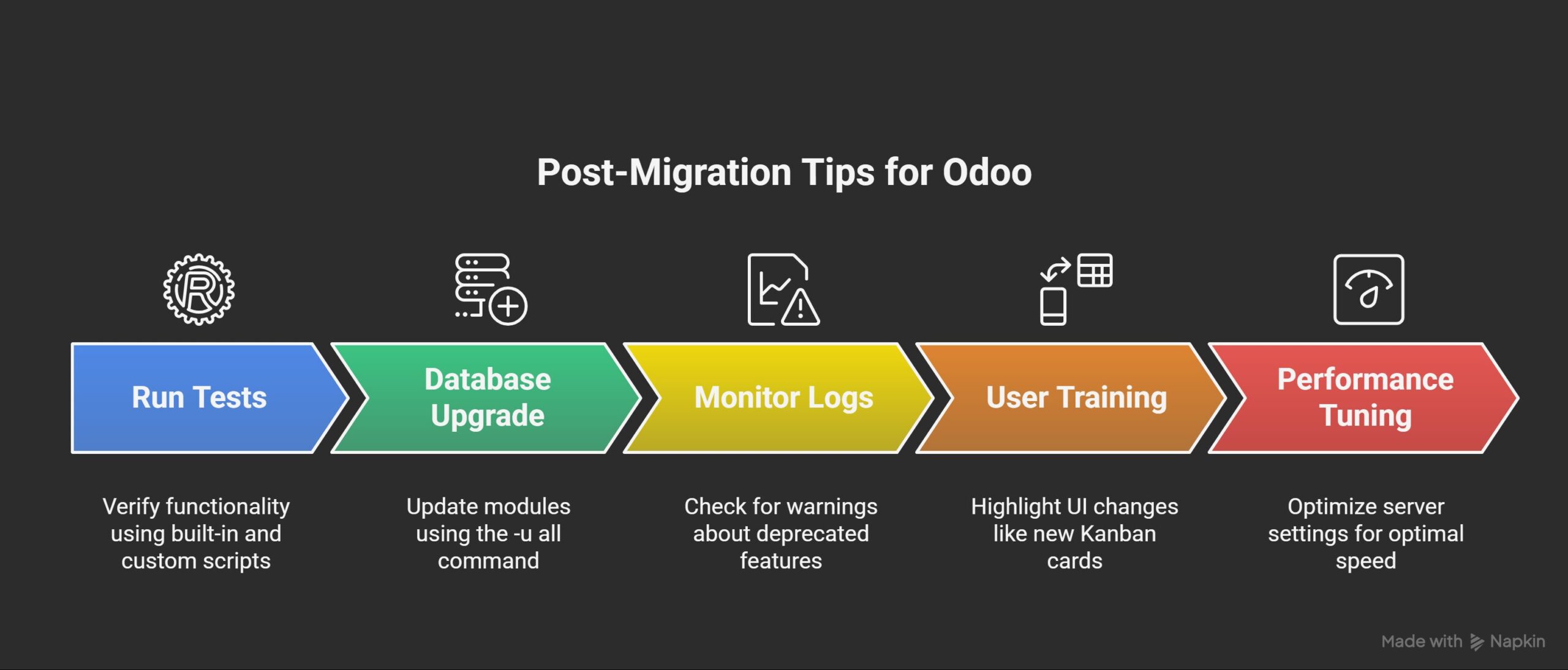
Post-Migration Tips
After applying these changes:
- Run Tests: Use Odoo’s built-in tests and custom scripts to verify functionality.
- Database Upgrade: Use the -u all command with –dev for module updates.
- Monitor Logs: Check for warnings about deprecated features.
- User Training: Highlight UI changes, such as the new Kanban cards.
- Performance Tuning: Odoo 19’s optimizations may require server tweaks for optimal speed.
Conclusion
Migrating from Odoo 18 to 19 is a strategic move that future-proofs your ERP system. By addressing these technical steps— from UoM and group changes to field renamings—you’ll achieve a robust upgrade. Remember, patience and testing are key to a successful Odoo migration. If you encounter issues, consult our Odoo’s official migration guide or seek expert help.
Stay tuned for more Odoo tips! If you’ve migrated successfully, share your experiences in the comments.
Frequently Asked Questions
Get Odoo Consultation







AUTHOR
Odoo
Neha Negi, Presales and Business Associate Head at Ksolves is a results-driven ERP consultant with over 8 years of expertise in designing and implementing tailored ERP solutions. She has a proven track record of leading successful projects from concept to completion, driving organizational efficiency and success.
Share with